The planet is warming up – since 1906, the average surface temperature has risen by almost 0.9°C. In the sensitive Polar regions this number is even greater, with average temperatures reaching up to 4°C higher than those recorded 50 years ago. However, today scientists prefer to use the term ‘climate change’ rather than global warming. This is because the term climate change encompasses extreme weather, habitat destruction, and rising sea levels that happen as a result of rising temperatures. Moreover, these events aren’t set to occur in some distant future – they’re happening right now, especially in our planet’s most delicate ecosystems. In this article, we talk about the causes and effects of pollution and how they impact the North and South Poles.
The effect of climate change on the Arctic and Antarctic
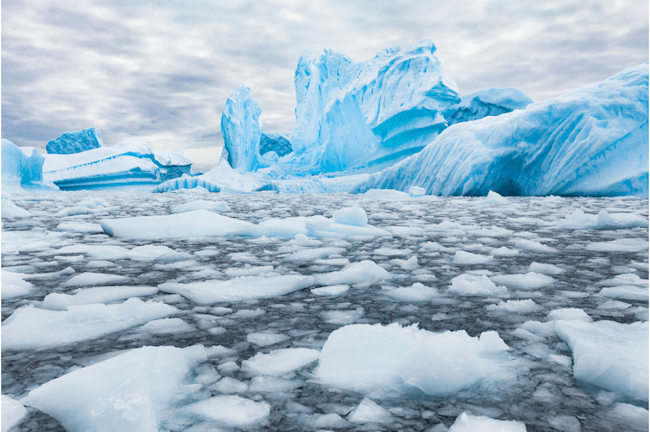

Globally, ice is melting – especially in the North and South Poles, including the ice sheets that cover much of West Antarctica and Greenland. This causes the sea level to rise. Today, the oceans are rising approximately 0.13 inches a year – and it’s only getting faster. However, these shifts don’t just affect the Poles; when the climate changes in these delicate regions, it has a knock-on effect across the world. For instance, average rain and snowfall have risen globally, increasing the likelihood of extreme flooding. However, these extreme climatic shifts are not confined to precipitation; some areas are experiencing extreme droughts, causing fires and drinking water shortages.
Rising temperatures don’t just affect the weather and terrain – they also have a significant impact on wildlife. As temperatures change, many species migrate further north to cooler areas. However, not all animals have the capacity to migrate. In the Poles, vanishing ice has threatened species like the Adélie penguin, whose populations have reduced by 90%. Scientists estimate that polar bear populations will be lower than 10,000 by 2050.
Causes and effects of pollution on ice melt
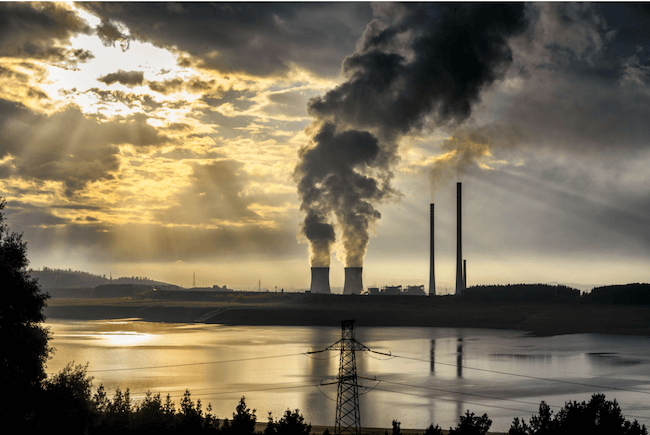

But what is causing climate change? Now, scientists unanimously agree that human activity is directly responsible. The primary cause is burning fossil fuels, which results in the accumulation of greenhouse gases. Burning oil, coal, and gas traps heat in the atmosphere, increasing temperatures and causing glaciers and ice sheets to melt. Furthermore, drilling for fossil fuels is also a significant contributor to climate change. These processes emit methane, which locks in heat even more effectively than carbon dioxide.
Besides the causes and effects of pollution described above, glacial melt has other important impacts on climate change. This is because ice melt exposes the earth beneath. Glaciers themselves are capable of absorbing 20% of the sun’s heat and reflect back the remaining warmth. But if the earth is exposed, the glacier reflects less heat, trapping more warmth in the atmosphere. Therefore, glacial melt is a cause and a symptom of global warming.
Protecting the glaciers and ice caps
Now, it is crucial that we do our part to help reduce the causes and effect of pollution. It is important to understand how our individual actions impact the environment and what we can do to reduce our carbon footprint. For instance, choosing to drive less is an important step towards changing habits and limiting our effect on the environment. However, there are also important steps we can take as a society. By supporting the development of new renewable energy sources, we can attempt to reverse the causes and effects of pollution – but we must act now.
No comments yet
There are no comments on this post yet.






Leave a comment